The escalating tension between Israel and Iran has rung alarm bells for the entire maritime shipping world, placing significant emphasis on important sea lanes and changing the patterns of international shipping. Between threats to the Strait of Hormuz and Houthi-backed attacks throughout the Red Sea, maritime shippers and insurers are experiencing increased exposure, cost, and uncertainty in freight markets. This blog examines six main impacts of this conflict on maritime shipping and global supply chains.
1.Rising Risk in Critical Trade Routes.
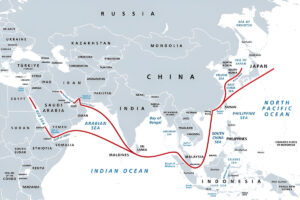
The Strait of Hormuz
Iranian officials have openly entertained the idea of closing or partly closing the Strait of Hormuz—a choke point that sees about 20 million barrels per day of crude oil pass through (1/5 of all crude oil exports worldwide), in addition to almost 30% of all liquefied natural gas exports. This would force tankers to sail around Africa, drop availability, and spark a rise in hydrocarbon prices. Though there have been historic examples of intimidation, the Strait has never completely closed. Still, the threats alone have created jitters in the market, precipitating a 7% increase in Brent crude in mid-June 2025.

The Red Sea
In the meantime, Iran’s ally—the Houthi movement in Yemen—has escalated attacks against vessels in the southern Red Sea and Bab el-Mandeb Strait that connect the Mediterranean (via the Suez Canal) to the Indian Ocean, which are the conduit for about 12% of global trade by volume. In response to waves of missile attacks and drone strikes, many shipping lines have temporarily suspended transits through the Red Sea, and instead opted to make a prolonged detour around the Cape of Good Hope.
2. Increased Shipping Costs
Insurance Rates Premiums for war‑risk insurance for voyages through the Strait of Hormuz and the Red Sea have increased dramatically. Underwriters now demand premiums as high as 1%–2% of a vessel’s insured value for a single trip—that is up from about 0.1% as a pre-war baseline. For a $100 million tanker, this means $1 million–$2 million more for the shipping costs, which affects both owners and charterers alike.
3. Volatility in Freight Rates
Frenzy in the Tanker Market
Growing fears of disruption to Middle Eastern oil supplies have pushed very large crude carrier (VLCC) freight forward agreements (FFA) above $40,000/day for July fixtures—over 50% jump month-on-month. For a brief window, spot rates from the Gulf to Asia ranged above $31,000/day as owners deliberately withheld tonnage waiting for higher rates.
The Dry Bulk Rollercoaster
On June 14, 2025, the Baltic Dry Index (BDI)—a barometer of bulk commodity shipping—shot up almost 10%-a a high not seen in 8 months. Ship owners remained wary of getting vessels on a route that had been changed in favour of the BDI. Yet the hint of de-escalation can bring immediate and severe corrections, making rate forecasting an exercise fraught with uncertainty.
4. Reconfiguring Shipping Routes
Increasing Detours
We are seeing more container, reefer, and roll‑on/roll‑off operators moving around the Suez and Hormuz chokepoints altogether. This reallocation of global capacity will cause some deviation from planned scheduled loops, require some slot rebalances, and challenge port rotational planning especially for Asia–Europe trades.
Growing Importance of Other Hubs

If disruptions continue, transshipment hubs in Southeast Asia – like Singapore or Tanjung Pelepas in Malaysia – will see increased prominence as relay points. Likewise, Chinese ports like Shanghai and Ningbo could take advantage of diverted transits and provide bunkering and repair services for vessels not wishing to transit these high-risk corridors.
5. Supply Chain Disruptions

Cargo Delays and Diversions
Manufacturers and e‑commerce providers are beginning to divert shipments to ports in South Asia, Africa, and even Australia. The cargo and order delays are simply too much of a risk to remain with Middle Eastern shipping ports. Automotive logistics and cold‑chain participants are first to alter plans, particularly in the context of time and temperature sensitivities..
Broader Logistical Disorder
Cargo delays and unknown route issues have complicated supply chain issues even more, especially for economies reliant on Middle Eastern oil and natural resources. Stock availability, order cancellations, and, almost immediately, conversations around re-shoring will happen as organizations begin to build/risk dependence against geopolitical vulnerabilities.
6. Responses of the International Community
Security Advisories and Naval Deployments
Several maritime authorities, including the UK Maritime Trade Operations (UKMTO) and private entity Diaplous, have upped alerts for commercial ships lining sailing in the Gulf of Oman, the Strait of Hormuz, and the Red Sea. The authorities are recommending that commercial ships strictly follow best management practices. At the same time, the U.S. Fifth Fleet and the Royal Navy are sending naval warships to monitor shipping lanes for commercial trade and conduct freedom-of-navigation exercises.
Diplomatic Engagement
The push for reduced hostilities has ramped up following the maritime attack. European and U.S. envoys are related to regional actors to reduce the potential for a broader maritime action that would disrupt global security and the economy. However, systemic change is slow to follow.
Conclusion
The Israel-Iran maritime conflict has created a new era of maritime risk, characterized by increased premiums, unstable freight markets, and new shipping routes. A contingency plan is being created now for shippers, insurers, and supply-chain managers based on new shipping routes design-led systems reduction in supply chain impact through new and diversified ports as buoyant response. The situation is fluid and as new indicators emerge; stakeholders must monitor diplomatic developments and security vigilant maritime advisories in order to mitigate risks in relation to potential events.
